Categories
Troubleshooting Common Filtration Issues: The Dreaded Pressure Spike

You’ve spent countless hours defining your filter process application. You’ve worked with the filter supplier on every aspect of feasibility and pilot testing, installation, and start-up. You’ve had weeks of normal operation… HOW COULD THIS HAPPEN?
One of the most common causes of failure in filtration systems is pressure spikes. Operating at too high of a pressure can work against filtration by compressing the cake and pushing solids into the structure of the media. Exceeding the pressure limits can result in filter element:
- Fouling or plugging
- Collapsing
- Bursting
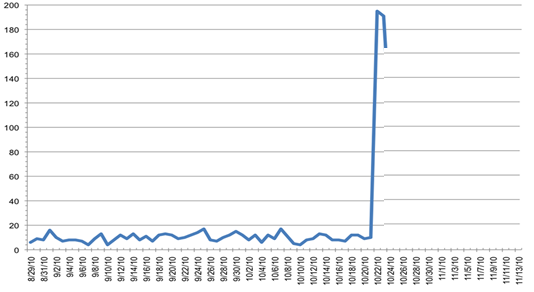
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes of pressure spikes, their impact on filtration systems, and provide step-by-step solutions to resume normal operation.
Understanding Pressure Spikes
A pressure spike is a sudden, often dramatic increase in pressure within a filtration system. These spikes can be momentary or sustained, but even brief spikes can cause significant damage to filter elements and compromise the entire filtration process.
The Impact of Pressure Spikes
- Cake Compression: High pressure can compress the filter cake, reducing its permeability and decreasing filtration efficiency.
- Media Damage: Excessive pressure can force particles into the filter media structure, causing irreversible fouling or even physical damage.
- Reduced Product Quality: Damaged or compromised filter elements may allow contaminants to pass through, affecting the quality of the filtered product.
- System Downtime: Addressing the consequences of a pressure spike often requires system shutdown, leading to production delays and increased costs.
Identifying the Cause of a Pressure Spike
When faced with a pressure spike, the first step is to determine its cause. Here’s a detailed approach:
1. Consult with Plant Operators
Talk to the plant operators to understand the conditions at the time of the spike. Several common conditions that might have played a major role include:
- Regulator or valve malfunction
- High solids concentration condition
- High flow rate condition
- Contamination (O-ring failure)
- Poor backwash
- Inadequate maintenance
Ask specific questions about any unusual events or observations leading up to the pressure spike.
2. Review Operational Parameters
Carefully examine the operational data for the filter installation. Verify that the following parameters are within the design operational range:
- Flow rate
- Pressure drop
- Filtrate quality
Look for any deviations from normal operating conditions that might have contributed to the pressure spike.
3. Inspect the Filtration System
Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the filtration system, paying close attention to:
- Valves and regulators
- Filter housing integrity
- Piping and connections
- Instrumentation accuracy
Common Causes and Solutions
Problem 1: Malfunctioning Valve or Regulator
Solution:
- Identify the faulty component through visual inspection and operational testing.
- Repair or replace the malfunctioning equipment.
- Calibrate the replaced or repaired component to ensure proper operation.
- Implement a regular maintenance schedule to prevent future malfunctions.
Problem 2: High Solids Concentration
Solution:
- Adjust upstream processes to reduce solids concentration if possible.
- Implement pre-filtration or additional settling stages to reduce the load on the main filter.
- Consider increasing the filter area or changing to a filter media with higher solids-holding capacity.
- Optimize backwash frequency and duration to handle higher solids loads.
Problem 3: High Flow Rate Condition
Solution:
- Verify that the system is not exceeding its designed flow rate capacity.
- Install or adjust flow control devices to prevent sudden surges.
- Consider parallel filtration systems to handle higher flow rates if demand has increased.
- Implement a variable frequency drive (VFD) on feed pumps to allow for better flow control.
Problem 4: Contamination (O-ring Failure)
Solution:
- Inspect all O-rings and seals in the system for signs of wear or damage.
- Replace any compromised O-rings with appropriate, compatible materials.
- Implement a regular inspection and replacement schedule for all seals and O-rings.
- Consider upgrading to more durable O-ring materials if failures are frequent.
Problem 5: Poor Backwash Performance
Solution:
- Review and optimize backwash parameters (frequency, duration, flow rate).
- Check for any obstructions in the backwash system.
- Consider using air-assisted backwash for more effective cleaning.
- Implement chemical cleaning cycles if standard backwashing is insufficient.
Problem 6: Inadequate Maintenance
Solution:
- Develop and implement a comprehensive preventive maintenance program.
- Train operators on proper maintenance procedures and the importance of adherence.
- Keep detailed maintenance logs and review them regularly to identify potential issues.
- Consider implementing predictive maintenance techniques using sensors and data analysis.
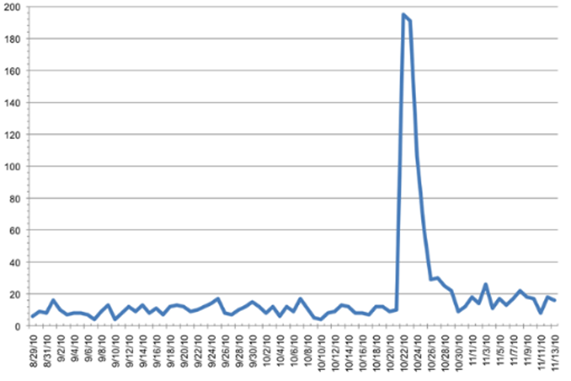
Recovering from a Pressure Spike
Once you’ve identified and addressed the root cause of the pressure spike, follow these steps to resume normal operation:
- Perform a Thorough Backwash: Repeat the backwash procedure and verify that the recovery pressure drop is within a few PSI of clean flow conditions.
- Chemical Cleaning: If pressure drop remains high after backwashing, soak and backwash filters with a process-compatible liquid or solvent. This can help remove deeply embedded contaminants.
- Verify Product Quality: Check that the product exiting the filter meets quality specifications. This step is crucial to ensure you have not collapsed or burst a filter element.
- Gradual Return to Operation: Slowly bring the system back to normal operating conditions, closely monitoring pressure, flow rate, and filtrate quality.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement enhanced monitoring for a period after the incident to ensure stable operation and catch any potential recurrence early.
You know you’re back to routine operation when:
- The pressure drop returns to near clean flow conditions
- Your product consistently meets quality specifications
- The system maintains stable operation over an extended period
Preventing Future Pressure Spikes
To minimize the risk of future pressure spikes:
- Implement Robust Process Controls: Use advanced control systems to maintain stable operating conditions.
- Regular System Audits: Conduct periodic reviews of the entire filtration system to identify potential issues before they escalate.
- Operator Training: Ensure all operators are well-trained in normal operations, troubleshooting, and emergency procedures.
- Data Analysis: Utilize historical operating data to identify trends that might predict future problems.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Adhere to a strict maintenance schedule, including regular replacement of wear parts.
Conclusion
Pressure spikes in filtration systems can be alarming, but with a systematic approach to troubleshooting and recovery, you can minimize their impact and prevent future occurrences. Remember, the key to success lies in quick identification of the root cause, implementing appropriate solutions, and maintaining vigilant monitoring of your filtration system.
Need further help troubleshooting filtration issues? We have a comprehensive lab and team of engineers & scientists that can help diagnose your most difficult issues. Contact us with questions today.
By staying informed, prepared, and proactive, you can ensure the longevity and efficiency of your filtration system, even in the face of challenging situations like pressure spikes.